Edge Vision

🔬 Edge Vision: Interactive Algorithm Comparison
Edge Vision is a Streamlit-based application for visually comparing classical edge detection algorithms like Sobel, Scharr, Laplacian, and Canny. With an intuitive interface and adjustable parameters, users can analyze how different methods influence edge detection results in real-time. It serves as both a learning tool and a benchmarking sandbox.
🚀 Launch the Interactive App
🎯 Motivation
In traditional computer vision, edge detection is a foundational step for object recognition and feature extraction. Comparing different detectors usually requires coding from scratch. Edge Vision solves this by offering an interactive tool to visually explore the strengths and limitations of each algorithm side-by-side.
🛠️ Technical Approach
- Frontend: Streamlit web interface for easy use and deployment.
- Algorithms: Implemented in OpenCV and wrapped in modular Python functions.
- User Controls: Allows customization of kernel size, thresholds, and direction (dx/dy).
- Display Engine: Renders edge results in a grid layout using Matplotlib.
✨ Key Features
- Interactive UI with full parameter control for each detector.
- Direct visual comparison of all outputs (Original, Sobel, Scharr, Laplacian, Canny).
- Custom
compare_all()pipeline with clean fallback and error handling. - Educational notes explaining the pros and cons of each method.
- Fully modular and extensible backend.
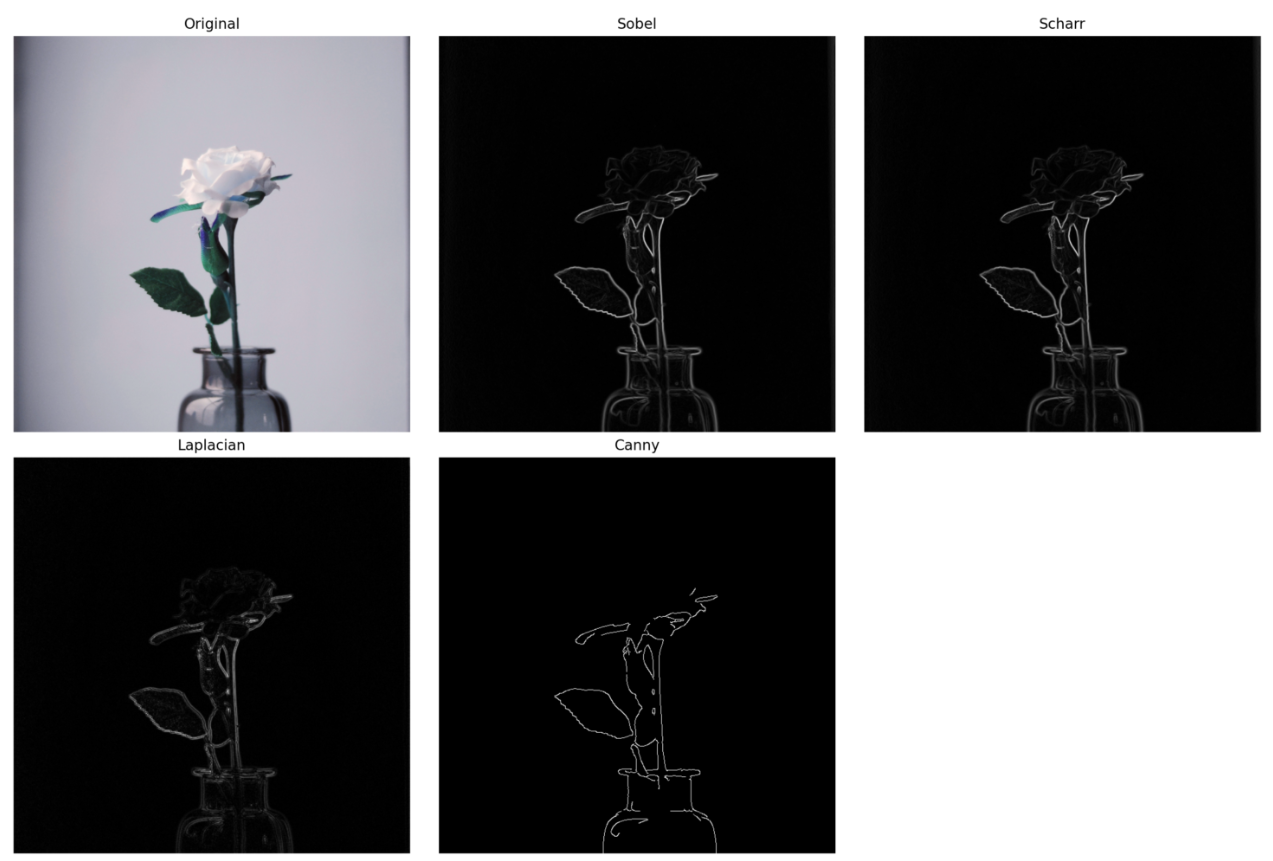
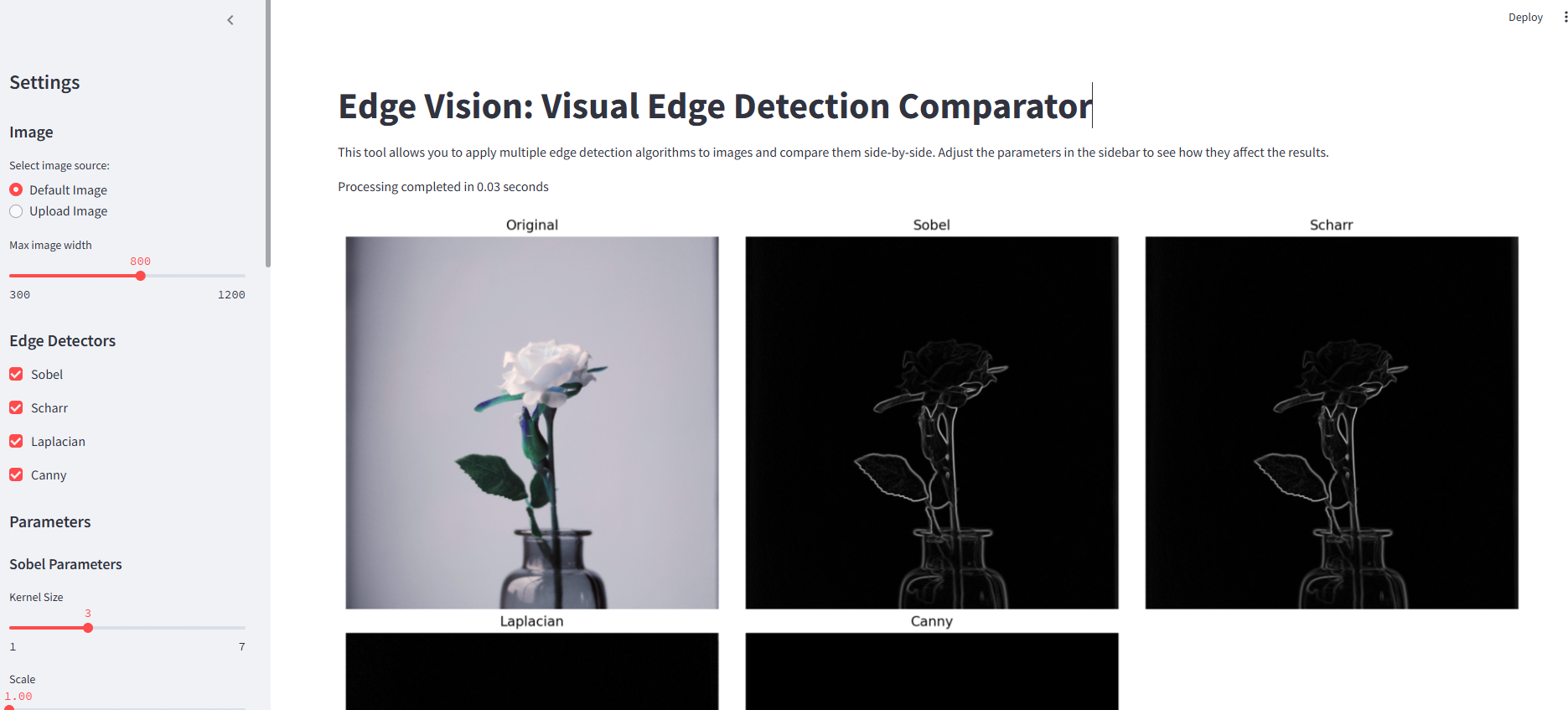
📊 Results & Gallery
The application clearly demonstrates that Canny consistently produces cleaner, more accurate results when tuned properly. Scharr offers sharper edges than Sobel, while Laplacian is more noise-sensitive but useful for symmetric edge detection.

💡 Reflection
This project sharpened my ability to bridge algorithmic vision concepts with user-centric interfaces. It also gave me practical experience with Streamlit app design, OpenCV filters, and scalable UI/UX structuring for educational tools. Future work could include adding noise robustness testing and integration of deep learning-based edge detectors.


